Early kingdoms

1600-year-old stone inscription from the era of Purnawarman, king of Tarumanagara, founded in Tugu sub-district of Jakarta.
References to the Dvipantara or Jawa Dwipa Hindukingdom in Java and Sumatra appear in Sanskrit writings from 200 BCE. The earliest archeological relic discovered in Indonesia is from the Ujung Kulon National Park, West Java, where an early Hindu statue of Ganesha from the 1st century CE was found on the summit of Mount Raksa in Panaitan Island. There is also archeological evidence of a kingdom in Sunda territory in West Java dating from the 2nd century, and according to Dr Tony Djubiantono, the head of Bandung Archeology Agency, Jiwa Temple inBatujaya, Karawang, West Java was also built around this time.

8th century Borobudur buddhist monument, Sailendra dynasty
A number of Hindu and Buddhist states flourished and then declined across Indonesia. By the time of the European Renaissance, Java and Sumatra had already seen over a millennium of civilization and two major empires. One such early kingdom wasTarumanagara, which flourished between 358 and 669 CE. Located in West Java close to modern-day Jakarta, its 5th-century king, Purnawarman, established the earliest known inscriptions inJava, the Ciaruteun inscription located near Bogor. On this monument, King Purnavarman inscribed his name and made an imprint of his footprints, as well as his elephant's footprints. The accompanying inscription reads, "Here are the footprints of King Purnavarman, the heroic conqueror of the world". This inscription is in Sanskrit2 and is still clear after 1500 years. Purnawarman apparently built a canal that changed the course of the Cakung River, and drained a coastal area for agriculture and settlement. In his stone inscriptions, Purnawarman associated himself with Vishnu, and Brahmins ritually secured the hydraulic project.
Three rough plinths dating from the beginning of the 4th century are found in Kutai, East Kalimantan, near Mahakam River. The plinths bear an inscription in the Pallava script of India reading "A gift to the Brahmin priests".
The political history of Indonesian archipelago during the 7th to 11th centuries was dominated by Srivijaya based in Sumatra, also Sailendra that dominated central Java and constructed Borobudur, the largest Buddhist monument in the world. The history of the 14th and 15th centuries is not well known due to scarcity of evidence. Two major states dominated this period; Majapahit in East Java, the greatest of the pre-Islamic Indonesian states, and Malacca on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula, arguably the greatest of the Muslim trading empires.
Medang

Prambanan in Java; built during the Sanjaya dynasty of Mataram, it is one of the largest Hindu temple complexes in south-east Asia.
Main article: Medang Kingdom
Medang or previously known as Mataram was anIndianized kingdom based in Central Java around modern-day Yogyakarta between the 8th and 10th centuries. The center of the kingdom was moved from central Java to east Java by Mpu Sindok. An eruption of Mount Merapi volcano or a power struggle may have caused the move.
The first king of Mataram was Sri Sanjaya and left inscriptions in stone. The monumental Hindu temple of Prambanan in the vicinity of Yogyakarta was built by Daksa. Dharmawangsa ordered the translation of the Mahabharata into Old Javanesein 996.
The kingdom collapsed into chaos at the end of Dharmawangsa's reign under military pressure from Srivijaya. One of the last major kings of Mataram was Airlangga who reigned from 1016 until 1049. Airlangga was a son of Udayana of Bali and a relative of Dharmawangsa re-established the kingdom including Bali under the name of Kahuripan.
Srivijaya
Main article: Srivijaya
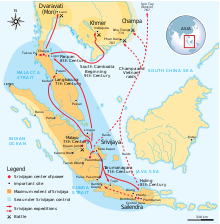
The empire of Srivijaya in Southeast Asia
Srivijaya was an ethnic Malay kingdom on Sumatra which influenced much of the Maritime Southeast Asia. From the 7th century CE, the powerful Srivijaya naval kingdom flourished as a result of trade and the influences of Hinduism and Buddhism that were imported with it.

As early as the 1st century CE Indonesian vessels made trade voyages as far as Africa. Picture: a ship carved onBorobudur, circa 800 CE.
Srivijaya was centred in the coastal trading centre of present day Palembang. Srivijaya was not a "state" in the modern sense with defined boundaries and a centralized government to which the citizens own allegiance. Rather Srivijaya was a confederacy form of society centered on a royal heartland. It was athalassocracy and did not extend its influence far beyond the coastal areas of the islands of Southeast Asia. Trade was the driving force of Srivijaya just as it is for most societies throughout history. The Srivijayan navy controlled the trade that made its way through the Strait of Malacca.
By the 7th century, the harbors of various vassal states of Srivijaya lined both coasts of the Straits of Melaka. Around this time, Srivijaya had established suzerainty over large areas of Sumatra, western Java, and much of the Malay Peninsula. Dominating the Malacca and Sunda straits, the empire controlled both the Spice Routetraffic and local trade. It remained a formidable sea power until the 13th century. This spread the ethnic Malay culture throughout Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula, and western Borneo. A stronghold of Vajrayana Buddhism, Srivijaya attracted pilgrims and scholars from other parts of Asia.
A series of Chola raids in the 11th century weakened the Srivijayan hegemony and enabled the formation of regional kingdoms based, like Kediri, on intensive agriculture rather than coastal and long distance trade. Srivijayan influence waned by the 11th century. The island was in frequent conflict with the Javanese kingdoms, first Singhasari and then Majapahit. Islam eventually made its way to the Aceh region of Sumatra, spreading its influence through contacts with Arabs and Indian traders. By the late 13th century, the kingdom of Pasai in northern Sumatra converted to Islam. At that time Srivijaya was briefly a tributary of the Khmer empire and later the Sukhothai kingdom. The last inscription dates to 1374, where a crown prince, Ananggavarman, is mentioned. Srivijaya ceased to exist by 1414, when Parameswara, the kingdom's last prince, converted to Islam and founded the Sultanate of Malacca on the Malay peninsula.
Singhasari and Majapahit

Wringin Lawang, the split gate shows the red brick construction, and strong geometric lines of Majapahit architecture. Located at Jatipasar, Trowulan,East Java.
Main articles: Singhasari and Majapahit
Despite a lack of historical evidence, it is known that Majapahit was the most dominant of Indonesia's pre-Islamic states. The Hindu Majapahit kingdom was founded in eastern Java in the late 13th century, and under Gajah Mada it experienced what is often referred to as a "Golden Age" in Indonesian history, when its influence extended to much of southern Malay Peninsula, Borneo, Sumatra, and Bali from about 1293 to around 1500.
The founder of the Majapahit Empire, Kertarajasa, was the son-in-law of the ruler of the Singhasarikingdom, also based in Java. After Singhasari drove Srivijaya out of Java in 1290, the rising power of Singhasari came to the attention of Kublai Khan in China and he sent emissaries demanding tribute. Kertanagara, ruler of the Singhasari kingdom, refused to pay tribute and the Khan sent a punitive expedition which arrived off the coast of Java in 1293. By that time, a rebel from Kediri, Jayakatwang, had killed Kertanagara. The Majapahit founder allied himself with the Mongols against Jayakatwang and, once the Singhasari kingdom was destroyed, turned and forced his Mongol allies to withdraw in confusion.
Gajah Mada, an ambitious Majapahit prime minister and regent from 1331 to 1364, extended the empire's rule to the surrounding islands. A few years after Gajah Mada's death, the Majapahit navy captured Palembang, putting an end to the Srivijayan kingdom. Although the Majapahit rulers extended their power over other islands and destroyed neighbouring kingdoms, their focus seems to have been on controlling and gaining a larger share of the commercial trade that passed through the archipelago. About the time Majapahit was founded, Muslim traders and proselytisers began entering the area. After its peak in the 14th century, Majapahit power began to decline and was unable to control the rising power of theSultanate of Malacca. Dates for the end of the Majapahit Empire range from 1478 to 1520. A large number of courtiers, artisans, priests, and members of the royal family moved east to the island of Bali at the end of Majapahit power.




















